The Wonderful Nerves In The Brain And Their Function
The nerves in the brain are often referred to as cranial nerve pairs. This is simply because they come in pairs, one on each half of the brain.
The complexity of the nervous system is astounding. Its many connections make this system the most important thing in the body. In this article we will talk about one of the most important components: The nerves in the brain.
The nerves in the brain, or pairs of nerves, originate from the base of the skull and reach their target areas through small openings through it. Thus, they communicate with all the peripheral areas. They are called “couples” because there is a nerve on both sides of the brain. Therefore, there are twelve nerves in the right hemisphere and twelve nerves in the left hemisphere.
Classifications of the nerves in the brain
The nerve pairs can be classified in different ways:
In relation to function
- Motor cerebral nerves. Brain nerves related to eye movements (3, 4 and 5) and related to movements of the tongue and neck (10 and 12).
- Sensory brain nerves. 1,2 and 8.
- Mixed brain nerves. 5, 7, 9 and 10.
- Parasympathetic cerebral nerves. 3 and 7.
The nerves in the brain in relation to position
There are some located above the brain stem (pairs 1 and 2); others in the upper part of the brainstem (pairs 3 and 4); those near the bridge (pairs 5, 6, 7 and 8); and finally those found in the lower part of the extended margin (pairs 9, 10, 11 and 12).
According to Bear, Connors and Paradiso, authors of the book Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain , the first two nerves in the brain are part of the central nervous system and the second part of the spinal nerves. They say that it is so “in the sense that they contain axons belonging to the peripheral nervous system.” Each of these nerves has fibers that perform several different functions.
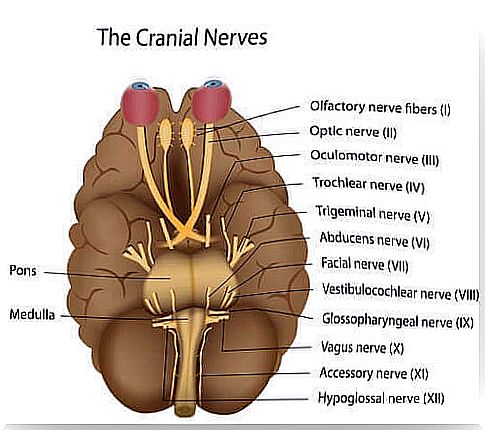
The nerves in the brain and their function
Brain nerve pairs 1
Axon types . Special sensory.
These are the shortest pairs of brain nerves, as the target area is close to the area coming from the brain. They are also called the olfactory nerve. In addition, as the name indicates, it is responsible for carrying nerve information related to odor.
The nerves in the brain: Cerebral nerve pairs 2
Axon types . Special sensory.
This nerve originates from the midbrain. And like the one we mentioned earlier, it has afferent fibers that transport nerve impulses from sensory organs in the central nervous system. Their function is to pass on visual information.
Cerebral nerve pair 3
Axon types . Somatic motor and visceral motor.
This nerve has another name: Nervus oculomotorius. It is responsible for the movements of the eyes and eyelids. In addition, it handles parasympathetic control of the size of the pupils.
The nerves in the brain: Cerebral nerve pairs 4
Axon types . Somatic motor skills.
This fourth originates from the midbrain. It goes by the name nervus trochlearis . It also handles the movement of the eye and sends signals to the eye’s superior oblique muscles.
Cerebral nerve pair 5
Axon types . Somatic sensory and somatic motor skills.
This is known as the triple nerve and has motor and sensory functions. First of all, at a motor level, it sends orders to the muscles responsible for chewing. And in addition, on a sensory level, it collects tactile, pain-related and proprioceptive information from the mouth and face.
The nerves in the brain: Cerebral nerve pairs 6
Axon types. Somatic motor skills.
This nerve pair is called the abducens nerve . They are responsible for the eyes’ ability to abduct, that the eye moves towards the opposite side of the nose. Isn’t it amazing?
Cerebral nerve pair 7
Axon types . Somatic sensory and somatic motor skills.
This is also known as the face pair. This is because they are responsible for the movement of the muscles for facial expressions. In addition, they also handle the sense of taste in the upper two thirds of the tongue. It also sends orders to the lacrimal and salivary glands.
The nerves in the brain: Cerebral nerve pairs 8
Axon types. Special sensory.
This is the auditory and equilibrium nerve. It is responsible for the senses of hearing and balance, receives information about what we hear, and our physical location.
Cerebral nerve pair 9
Axon types . Somatic motor, visceral motor, special sensory, and visceral sensory.
These are called the glossopharyngeus nerve . They are a mixing nerve, and from the name one can deduce some of the functions:
- Movement of the muscles in the neck.
- Parasympathetic control of the salivary glands.
- Detect changes in blood pressure in the aorta.
- The sense of taste in the first third of the tongue.

The nerves in the brain: Cerebral nerve pairs 10
Axon types. Visceral motor skills.
This is called the vagus nerve. It is responsible for the parasympathetic control over the heart, lungs and internal organs. In addition to this , it transmits the sensation of visceral pain, the movements of the neck muscles, and also receives information about taste.
Cerebral nerve pair 11
Axon types. Somatic motor skills
This is called nervus accessorius . This handles movement in the muscles of the neck and neck.
Cerebral nerve pair 12
Axon types. Somatic motor skills.
This is called the hypoglossus nerve . This pair of brain nerves contributes to swallowing. In addition, it is responsible for the movement of the tongue, and works with cerebral nerve pairs 9 and 10. Thanks to this pair, swallowing can be performed optimally.
As you can see, any damage to the nerves in the brain can mean serious problems for bodily function and even our survival. Neurological disorders can manifest themselves when an injury occurs in the body.
We hope this has helped you understand and appreciate these important nerves in our brain much more!